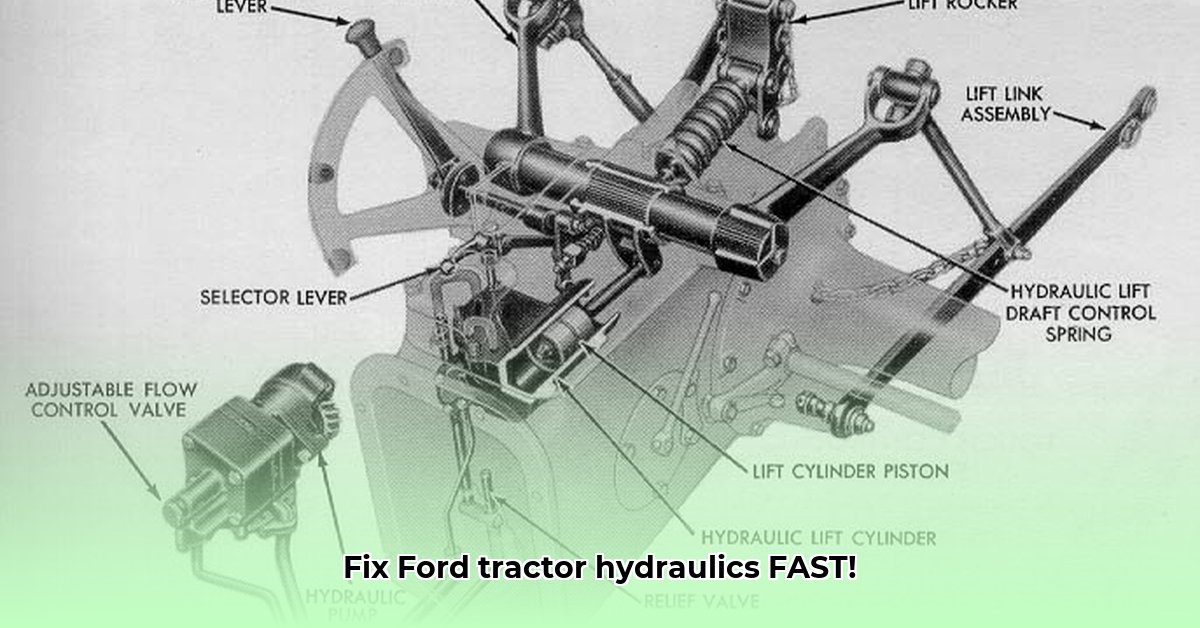
Hydraulic problems can quickly sideline your Ford NAA or 1520 tractor. This guide provides step-by-step instructions for diagnosing and fixing common issues, from simple leaks to more complex pump problems. Whether you're a seasoned mechanic or a novice, this guide empowers you to get your tractor back in the field. For more Ford tractor specifications, check out this helpful resource: Ford Tractor Specs.
Diagnosing Lifting Issues in Your Ford Tractor
A sluggish or failing hydraulic lift can stem from several sources. The most common culprits are worn seals (gaskets), a failing hydraulic pump, or issues within the auxiliary hydraulic circuits. Think of your tractor’s hydraulic system as its circulatory system – a problem in one area can impact the whole. Let's address these potential problems:
Gasket Troubles: A Frequent Culprit
Gaskets, those vital rubber seals, prevent hydraulic fluid leaks. In older Ford NAA models, gasket failure between the lift cylinder and its cover is a common cause of lift problems. A leaky gasket reduces hydraulic pressure, resulting in a weak or non-functional lift. Regular inspection is crucial; preventative replacement can avoid costly repairs.
The Failing Hydraulic Pump: A Gradual Decline
A weakening hydraulic pump often manifests as a gradual decrease in lifting power. The fluid level might appear normal, but the pump's reduced output causes a diminished lift. This is akin to an aging engine – it runs, but lacks its former strength. A pressure test is essential for confirming pump failure; this usually requires specialized tools and expertise.
Auxiliary Hydraulic Circuits: Potential Points of Failure
Improperly connected auxiliary hydraulic circuits (used for attachments) can severely disrupt the entire hydraulic system. Incorrect routing, often seen on Ford 1520 models, can create a shortcut that disrupts normal fluid flow. Similar to a short circuit in your home's electrical system, this can cause widespread problems.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Guide
Let's get that lift working again! Follow these steps to diagnose and address common Ford tractor hydraulic issues:
Check the Lift Cover Gasket: Carefully inspect the gasket on the lift cylinder for damage. Replace if necessary. This is a straightforward, often effective first step.
Verify Hydraulic Fluid Levels: Ensure the hydraulic fluid reservoir is full. Low fluid is a frequent cause of weak lifts.
Inspect Hydraulic Lines and Connections: Look for leaks, cracks, or worn spots in all hydraulic lines and connections. Repair or replace any damaged components.
Examine Auxiliary Hydraulic Circuits: Double-check all auxiliary connections for correct routing and secure fittings. Consult your owner's manual for proper configuration.
Conduct a Hydraulic Pump Pressure Test: If problems persist, a pressure test is essential to assess pump health. This typically requires specialized tools.
Check Relief Valves (if applicable): A malfunctioning relief valve can lead to complete hydraulic failure. Ensure its proper operation if your model includes one.
Preventative Maintenance: Avoiding Future Headaches
Regular maintenance is paramount in preventing major hydraulic issues. A proactive approach considerably reduces the likelihood of costly repairs.
Regular Fluid Changes: Change hydraulic fluid annually (or as recommended in your owner's manual) using the correct type. This maintains system cleanliness and lubrication.
Gasket Inspections: Inspect the lift cover gasket every six months to identify and address wear before it leads to leaks.
Hydraulic Line Inspections: Inspect all hydraulic lines semi-annually for leaks, cracks, or damage. Address any issues immediately.
Auxiliary Circuit Inspections: Annually check auxiliary circuits to ensure correct connections and smooth fluid flow. A visual inspection can identify many problems.
Preventative Maintenance Schedule
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Fluid Change | Annually (or as needed) | Maintains system cleanliness, prevents pump wear. |
| Lift Cover Gasket Inspection | Every 6 months | Prevents leaks, ensures proper lift operation. |
| Hydraulic Line Inspection | Every 6 months | Early identification of potential leaks and damage. |
| Auxiliary Circuit Check | Annually | Ensures proper function of attachments. |
Implementing this preventative maintenance schedule significantly reduces the risk of major hydraulic problems, preventing costly downtime and repairs. Remember, a little preventative care now saves significant headaches later.